- Payment gateway
- Blog
- The Domino Effect of Late Payments: How Corporate Business Can Handle It
The Domino Effect of Late Payments: How Corporate Business Can Handle It
Late payment is an end-game issue for various businesses. Even big enterprises, which are typically better capitalised, having multi-tier supply chains, huge vendor bases, and tiered financial structures are struggling from this challenge. Late payment with such businesses has the potential to cascade through to operational efficiency, vendor relationships, regulatory compliance, and overall market reputation. One late payment by one supplier can trigger a chain of negative effects across an organisation’s supply chain. This issue is most pronounced in distribution and business services, where 87% of businesses are negatively impacted by late payments. Besides, an EU survey of B2B payments showed the average payment term duration increased from 51 to 55 days, and industry leaders were generally at the lower end of the long delays. In this article we will analyse this challenge and provide the tips on how to reduce late payments impact of the business processes.
The Scale of the Problem
Large businesses possess complex finance situations where even small delays would lead to massive financial backlog. Compared to small companies with manual handling of payment behaviour, large companies are founded on multi-department computerised processes and strict financial controls. Delay in payment to even one vendor or service provider will trigger a domino effect that will lead to operation slowdown, loss of partner trust, and loss of reputation. Studies recently conducted have identified administrative inefficiencies as one of the most prevalent causes of delay in payment by large companies. 36%, of large businesses, in one UK government report, attribute their lateness to pay onerous administrative procedures, including ‘no order, no payment’ policy. Such strict regulations, as much as they are meant to provide financial precision, more frequently than not lead to delayed payment to vendors, compelling vendors to look elsewhere for finance or cut service levels.
Late payment also carries legal and regulatory consequences. Tighter late payment legislation is being implemented in most jurisdictions where businesses are legally culpable for failure to honour contractual payment terms. In highly regulated healthcare and finance sectors, non-payment lags behind on account results in fines, audit, and loss of reputation. Businesses that fail to monitor chronic late payment will either become blacklisted by suppliers or remain uncompetitive because of an inability to handle money. Apart from intracompany problems, late payment also affects other external stakeholders. Late payment by a large business company can trickle down to suppliers, subcontractors, and other business firms that bank on timely payment. This instability can lead to overborrowing, project delays, and even business closure among supplier companies.
Strategies to Overcome Late Payment Problems
For timely tackling of the cause of late payment, major companies must adopt preventive initiatives enhancing monetary openness, optimising process efficiency, and consolidating better relations with their suppliers. The following measures, if adopted, can cut down the traps of late payments:

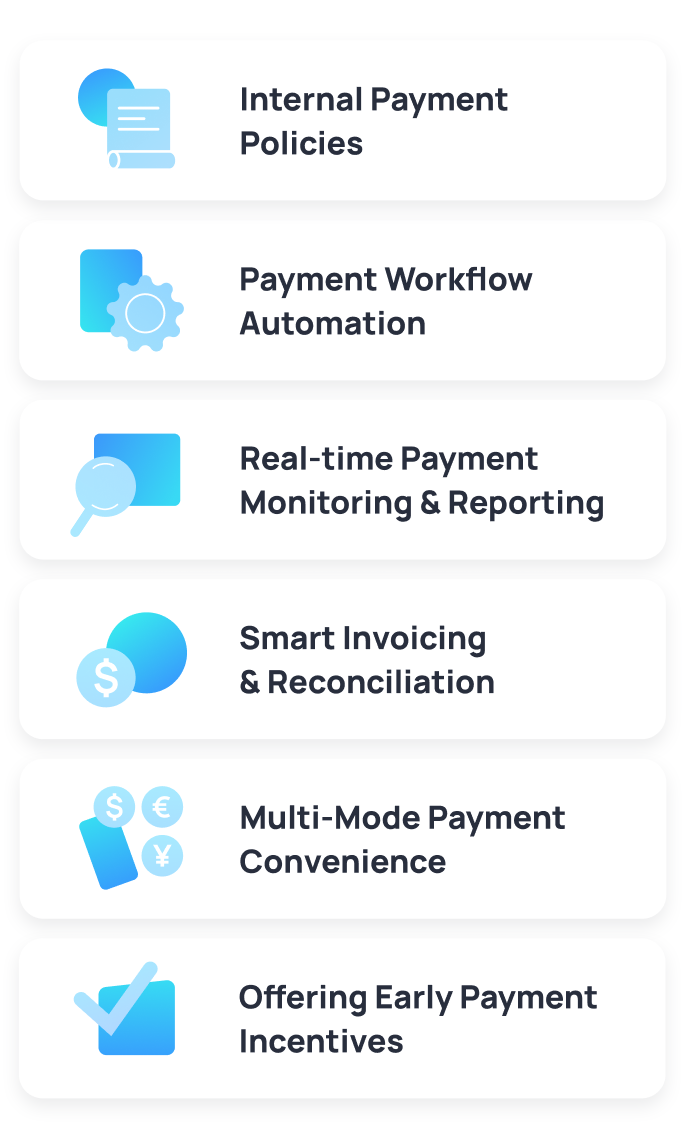
Internal Payment Policies
Having enforceable and clear payment policies is the best way to avoid delay. Organisations need to develop standard payment terms, institute approval processes, and have all the departments that make payments on the same page. Regular internal financial process audits also identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies in the system that cause delayed payments.
Payment Workflow Automation
Automation is necessary to avoid delays caused by manual processing. Through the use of systems that pre-schedule payments and automatically execute transactions, companies can reduce human errors to a large extent and make timely payments. These solutions also provide a formal approval process, guaranteeing compliance as well as reducing the time for transactions.
Real-time Payment Monitoring and Reporting
Transparency of the payment cycles is essential to prevent delays. Real-time tracking software helps organisations monitor the payment status, receive alerts for pending payments and due payments, and trigger on-time processing. Predictive analytics can even be employed to forecast cash inflow patterns and schedule payments in advance to prevent failures at due dates.
Smart Invoicing and Reconciliation
Electronic billing systems streamline the entire payment process by reducing paperwork, less room for error, and ensuring invoices are prepared, dispatched, and processed on time. In addition, reconcile functions automatically guarantee matching of incoming payments against invoices and identify discrepancies in a timely manner so that corrections are made immediately.
Multi-Mode Payment Convenience
Offering various payment methods to partners and suppliers can speed up the transaction velocity. Companies must make payments through various channels, including direct bank transfers, e-wallets, and recurring debit arrangements. This variety allows suppliers to receive payments in their preferred channels, lowering disputes and processing time.
Offering Early Payment Incentives
Launching them in the form of early payment discounts can allow companies to maintain supplier relationships in good standing while optimising cash flows. Offering financial incentives to suppliers for early payment can reduce the risk of late payment while giving vendors liquidity to carry on business.
Industry Use Cases
Technology & software and e-commerce are the industries most affected by delayed payments. Both these sectors have their specific issues, but through the proper use of payment mechanisms, companies can control risk and process money effectively.
Technology & Software
The technology and software industry is one that is very reliant on subscription-based revenues, software licensing agreements, and cloud providers. Payment delays have the potential to be a hurdle when it comes to financial stability, contract renewal, and vendor relationships.
Recurring billing models
There are recurring bill cycles in the majority of technology firms, and delayed payment from enterprise clients will impact the cash flow on a month-to-month basis. There are ways for companies to avoid any inconvenience while receiving payments timely by automating bills and establishing smart billing measures.
Timely payment to vendor and service provider
Technology firms often use third-party vendors to provide cloud computing, security, and software integration. Timely payment to the vendor must be ensured to prevent service disruption and ensure business continuity.
Adherence to customer payment
Software licensing firms must have robust payment enforcement systems, such as contract-based conditions and automated reminders, to reduce the likelihood of delayed payment.
E-commerce
E-commerce businesses have significant areas of pain in processing supplier payments, transaction charges, and refunds. Payment delay in e-commerce may impact inventory, supplier relations, and customer satisfaction.
Supplier payment cycles
Online companies depend on suppliers to replenish inventory. Slow payment to suppliers can result in stockouts, which translate into lost sales and low customer satisfaction. Automatic payment to suppliers ensures consistent stock levels.
Marketplace settlements
Marketplaces that handle millions of transactions on a daily basis must settle with merchants and sellers in a timely manner, which is very crucial. Not settling on time will influence platform trust and prevent sellers from conducting additional business.
Management of chargebacks and refunds
Online businesses must address customer chargebacks and refunds every day. Refund transactions ought to be streamlined and not encumbered with any hitch so as not to disrupt cash flows and policy regulation compliance.
Conclusion
Big businesses focusing on improving internal controls, leveraging automation, and streamlining supplier relationships will be better placed to overcome payment challenges. Timely, trouble-free payments form the foundation of trust, stability, and long-term success. By prioritising efficiency and stability, major corporations can create strategic advantage, ensuring that late payment doesn’t impede business growth or supply chain reliability. Want to find out more about how to optimise your payments? Fill out the form below and our experts will help you.